Grim and Malaria: Malaria is a life-threatening disease caused by parasites that infect people through mosquito bites. It is most prevalent in tropical and subtropical locations, like Africa, Asia, and Latin America.
What are The Types of malaria?
- Plasmodium falciparum: Plasmodium falciparum is responsible for almost all malaria-related fatalities worldwide. It manifests with severe symptoms and can lead to issues like cerebral malaria, which affects the brain and is fatal if left untreated.
- Plasmodium vivax: Plasmodium vivax is the most common malaria parasite outside of Africa because a reprise can occur months or even years after the first infection.
- Plasmodium ovale: Plasmodium ovale is less frequent than other species, yet it can still cause repeated bouts of malaria if not treated correctly
- Plasmodium malaria: Plasmodium malaria causes fewer symptoms than other kinds of malaria, but it can stay in circulation for a long time.
What are the causes of malaria?
Transmission- Malaria is transmitted by the following steps:
- Mosquito Bite: When an infected mosquito bites a human, the malaria parasites enter the circulation.
- Parasite Multiplication: The parasites spread to the liver, where they begin to grow and mature.
- Red Blood Cell Invasion: Mature parasites are discharged into the circulation, infecting red blood cells and reproducing.
- Symptom Onset: As the infection grows, people may get symptoms like fever, chills, and exhaustion.

What are the Common symptoms?
- Fever: One of the most common symptoms of malaria is a high fever.
- Headaches: Malaria patients frequently have severe headaches.
- Fatigue: Malaria can induce too much fatigue and weakness, making it difficult to carry out regular tasks.
- Muscle Pain: Pains in the muscles are common, especially in the back and joints.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Many people experience nausea, vomiting, and a lack of appetite.
Severe Symptoms
- Cerebral Malaria: This illness affects the brain and can result in attacks, unconsciousness, and brain damage.
- Severe Anemia: Malaria can cause a large reduction in red blood cells, resulting in anemia and organ failure.
- Respiratory Distress: Some people may have trouble breathing owing to excess fluid in their lungs.
The Link Between Grim and Malaria
- Definition of Grim: Grim refers to a marginalized and frequently socially excluded group that has several obstacles, particularly poor access to healthcare and education.
- Historical Context of Grim: The Grim population has historically suffered disadvantage and marginalization, leading to inequities in health outcomes and access to critical services.
- Relation Between Grim and Malaria: The Grim population’s socioeconomic position, housing circumstances, and limited access to healthcare services make them especially affected by malaria.
Impact on Communities
- Vulnerability to Malaria: Grim populations frequently live in locations with a large mosquito population and low sanitation, which increases their risk of malaria infection.
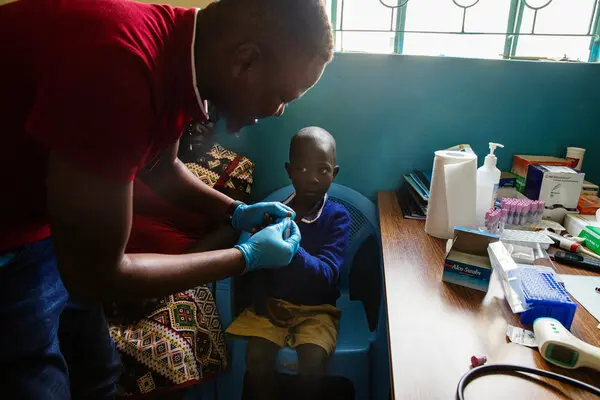
- Healthcare Challenges: Malaria diagnosis and treatment are delayed due to a lack of access to healthcare services and resources among Grim people.
- Economic Implications: The burden of malaria-related disease and medical expenses promotes poverty and social inequities in Grim communities.
Efforts in Combating Malaria Among Grim Populations
- Awareness Campaigns: Educational efforts aimed at Grim populations improve knowledge about malaria transmission, preventative methods, and the significance of getting immediate medical attention.
- Access to Healthcare: Improving access to healthcare services, particularly diagnostic testing and antimalarial treatment, is critical for lowering malaria death and illness in Grim communities.
- Research and Development: Investing in research to create new tools and strategies customized to the requirements of Grim communities is crucial for effective malaria control.
Community Engagement and Empowerment
- Role of Community Leaders: Empowering Grim community leaders to advocate for better healthcare access and resources boosts their resistance to malaria.
- Education and Training: Education and training on malaria prevention and control techniques provide Grim people with the knowledge and skills they need to protect themselves and their loved ones.
- Supportive Policies: Implementing measures that address socioeconomic factors that influence health and enhance fairness in healthcare delivery can assist in reducing malaria prevalence in Grim communities.
Future Directions in Addressing
- Innovative Approaches: Innovative techniques, such as mobile health technology and community-based surveillance systems, can help improve malaria control efforts in Grim contexts.
- Global Partnerships: Collaboration among governments, NGOs, and international organizations is critical for deploying resources and knowledge to combat malaria in Grim communities.
- Technological Solutions: Advances in diagnostic techniques and vector management approaches show promise for improving malaria prevention and treatment results in Grim communities.
HEALTHY FOOD
- Nutrient-rich foods: Consuming a range of nutrient-dense meals, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean meats, and healthy fats, can supply the vital vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants required for proper immune function.
- Iron-rich foods: Vitamin A helps to maintain a healthy immune system and guard against infections. Carrots, sweet potatoes, spinach, and mangoes are all good sources of vitamin A.
- Vitamin A Sources: Malaria can cause anemia by destroying red blood cells. Iron-rich foods including leafy greens, legumes, fortified cereals, and lean meats can help prevent or cure anemia while also promoting general health.
- Vitamin C-rich foods: Vitamin C is recognized for its immune-boosting and antioxidant qualities. Citrus fruits, berries, bell peppers, broccoli, and tomatoes are high in vitamin C, which can aid improve the immune system.
- Hydration: Staying hydrated is crucial, especially in malaria-prone areas. Drinking plenty of water and eating hydrating meals like fruits and vegetables can help avoid dehydration and improve overall health.
Conclusion
The link between Grim culture and malaria highlights the need for specific treatments that overcome socioeconomic inequality and cultural obstacles. We can make great progress in lowering the malaria burden among Grim communities by focusing on community participation, empowering local leaders, and implementing creative solutions.
Read More: GA Eye Disease Symptoms: A Comprehensive Guide
Frequently Asked Questions
How does poverty affect the frequency of malaria in Grim communities?
Living conditions are impacted by poverty, which can result in inadequate housing, limited access to sanitary facilities and clean water, and a shortage of healthcare
How do cultural values influence Grim communities’ views towards malaria prevention?
Culturally responsive malaria control tactics are important because they can influence how people perceive the origin of sickness, how they seek treatment, and whether they adopt prevention measures.
What are some challenges in providing healthcare to malaria-affected remote Grim populations?
Logistical restrictions include limited transportation infrastructure and geographical remoteness.
