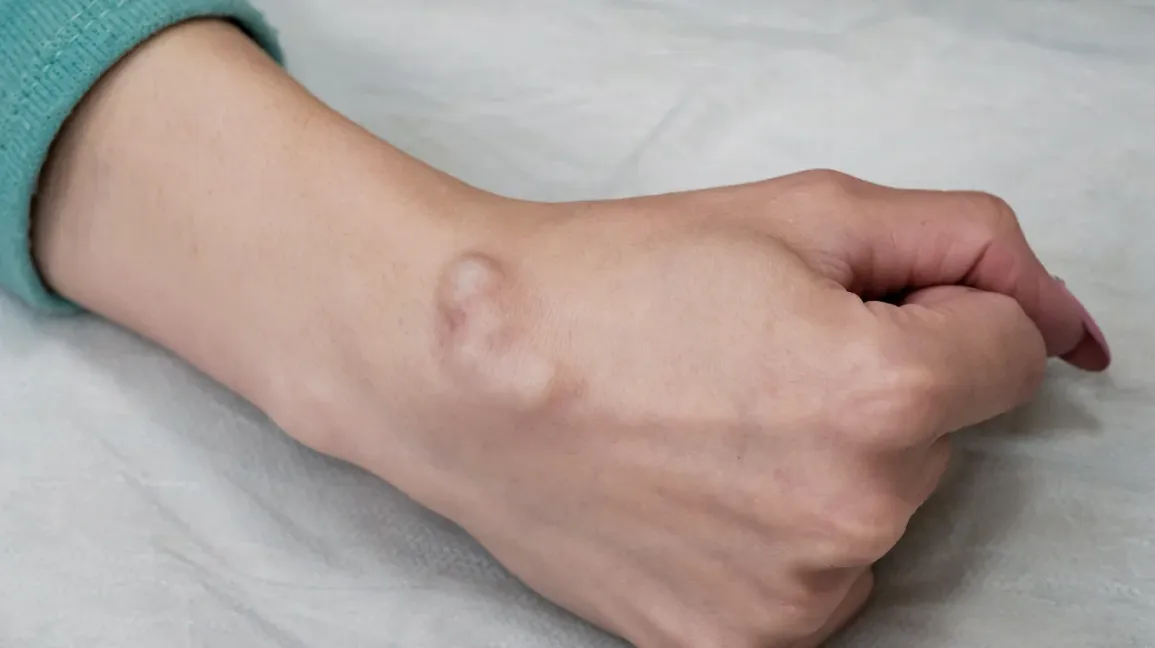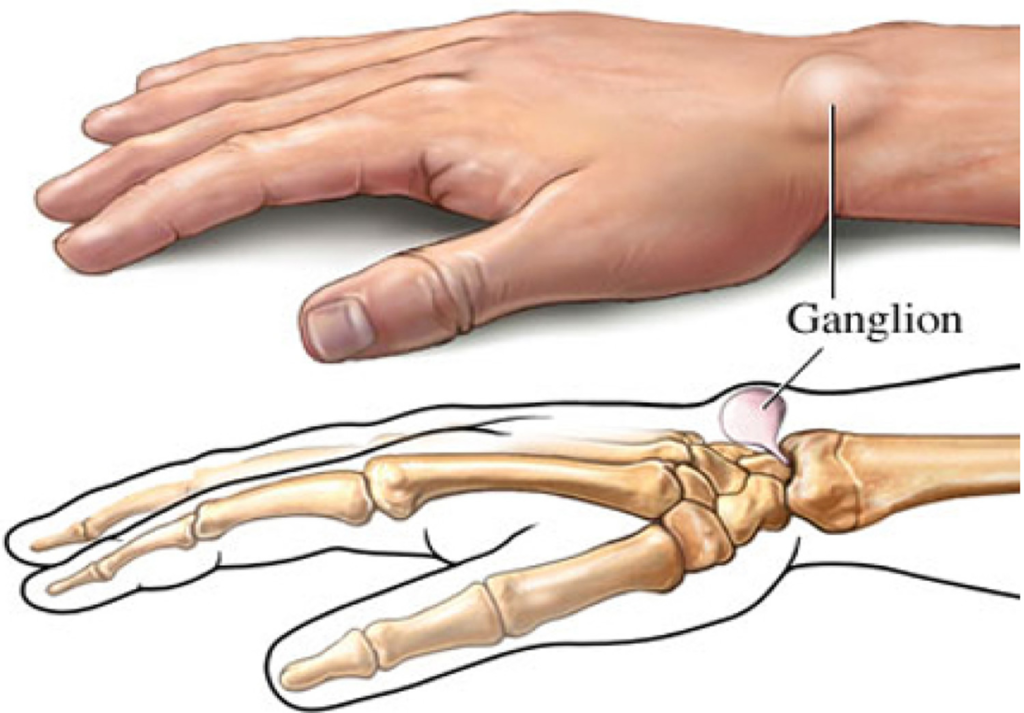
Ganglion Cyst Vitamin Deficiency: Ganglion cysts are noncancerous lumps that form on the tendons or joints of your wrists or hands. Although they are mostly harmless, they can cause discomfort or block joint mobility. Vitamin deficiency, on the other hand, is a disorder caused by a lack of important nutrients, which can result in a variety of health problems.
Characteristics and Symptoms of Ganglion Cyst Vitamin Deficiency
Ganglion Cyst Vitamin Deficiency are sacs filled with fluid that seem like bumps under the skin. They range in size from a pea to an inch in diameter. Cysts are usually round or oval in shape and can feel hard or spongy to the touch. Symptoms could include:
- A conspicuous bump.
- Pain or discomfort, particularly during the motion of joints.
- Tingling or numbness may occur if the cyst pushes on a nerve.
Common Locations
Ganglion cysts are most usually found on the back of the wrist, although they can also form on the palm side, the base of the fingers, and the top of the foot.
Risk Factors
Several factors may raise the likelihood of developing ganglion cysts, including:
- Possible causes of wrist or hand pain include overuse or repeated motions
- previous joint or tendon injuries
- Certain medical diseases, such as arthritis
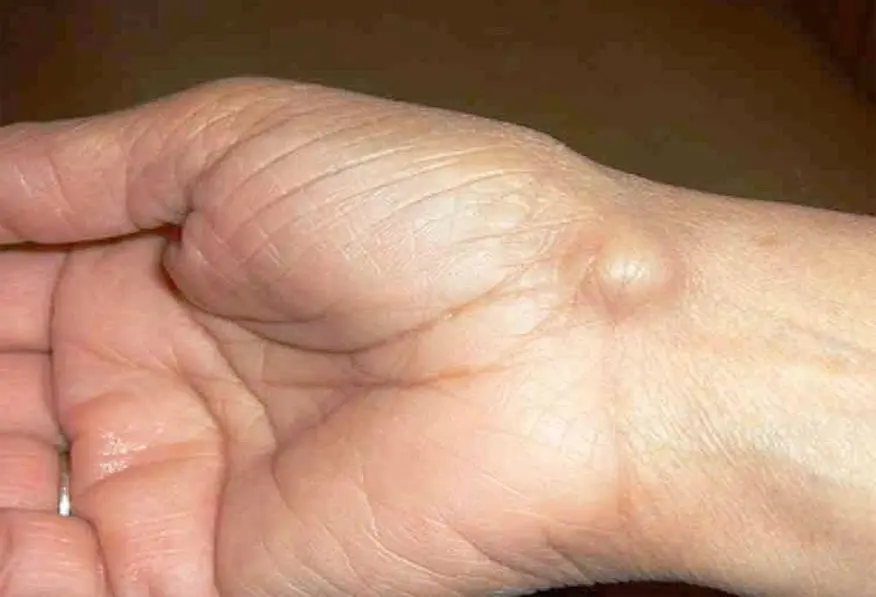
Causes of Ganglion Cyst Vitamin Deficiency
Overuse and Injury: Ganglion Cyst Vitamin Deficiency can occur when joints and tendons are subjected to frequent or repeated tension. This is common in those who do repeated hand motions, such as typing or playing sports.
Genetics: Ganglion cysts may be caused by a hereditary predisposition since they tend to run in families.
Other Contributing Factors: Inflammation of joints or tendons, as well as underlying joint problems, may also contribute to the formation of ganglion cysts.
Understanding Vitamin Deficiency
Common Vitamin Deficiencies: Vitamin deficiencies arise when the body lacks vital vitamins owing to a poor diet, specific health problems, or lifestyle choices. Common shortcomings include:
- Vitamin D
- Vitamin B12
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin E
Symptoms of Vitamin Deficiency: Symptoms of vitamin insufficiency vary but frequently include:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Muscle cramps or pain
- Dry skin or brittle hair
- Slow wound healing
Long-Term Effects of Vitamin Deficiency: Long-term vitamin deficits can cause serious health concerns, such as:
- Osteoporosis (from lack of Vitamin D)
- Anemia (from lack of Vitamin B12)
- Scurvy (from lack of Vitamin C)
- Neurological issues (from lack of Vitamin E)

Types of Vitamins Essential for Health
- Vitamin D: Vitamin D is important for bone health because it promotes calcium absorption. It also affects immunological function.
- Vitamin B12: Vitamin B12 is required for nerve function and the formation of red blood cells. A deficit can cause neurological disorders and anemia.
- Vitamin C: Vitamin C is essential for tissue development and repair in the body. It also aids in the absorption of iron from plant-derived meals.
- Vitamin E: Vitamin E is an antioxidant that protects cells from harm. It’s also important for immunological function and skin care.
The Role of Vitamins in Joint and Tissue Health
- Importance of Vitamins for Connective Tissues: Vitamins help to maintain healthy connective tissues such as tendons, ligaments, and cartilage. They promote collagen formation, decrease inflammation, and aid in the healing of injured tissues.
- How Vitamins Help in Preventing Cysts: Healthy vitamin consumption can improve overall joint health and may help avoid the formation of ganglion cysts by lowering inflammation and improving tissue healing.
Vitamin Deficiency and Its Link to Ganglion Cysts
- Theoretical Connections: While there is little direct evidence linking vitamin shortages to ganglion cysts, several ideas claim that inadequate nutrition may damage tissue health, making cyst formation more likely.
- Scientific Studies and Evidence: Several studies have looked at the impact of vitamins on tissue health, but more study is needed to determine a direct link with ganglion cysts. For example, vitamin D has been demonstrated to lower inflammation, which may lessen the chance of cyst development.
- Case Studies: Some case studies have shown that individuals with ganglion cysts benefit from vitamin therapy, particularly those known to promote joint health.
Preventing Ganglion Cyst Vitamin Deficiency Through Diet
Foods Rich in Essential Vitamins: Including foods high in vital vitamins in your diet will help you maintain joint and tissue health. Examples include:
- Vitamin D: Fatty fish, fortified dairy products, and egg yolks
- Vitamin B12: Meat, dairy products, and fortified cereals
- Vitamin C: Citrus fruits, strawberries, and bell peppers
- Vitamin E: Nuts, seeds, and green leafy vegetables
Dietary Recommendations: A well-balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, lean meats, and whole grains will help you obtain all of the vitamins you need.
Supplements and Their Role: While food is the best source of vitamins, supplements can help address any nutritional shortages. Always consult with a doctor before beginning any new supplement program.
Treatment Options for Ganglion Cyst Vitamin Deficiency
Non-Surgical Treatments: Non-surgical therapy options for ganglion cysts include:
- Observation: Ganglion Cyst Vitamin Deficiency can sometimes resolve themselves without the need for therapy.
- Immobilization: Wearing a brace or splint might limit mobility and help the cyst shrink.
- Aspiration: when a doctor uses a needle to extract fluid from a cyst.
Surgical Options: If non-surgical therapies fail, surgery may be necessary to remove the cyst. This is generally recommended if the cyst causes severe discomfort or impairs joint function.
Role of Vitamin Supplementation in Treatment: Including vitamin supplements in a treatment plan may assist in improving tissue health and avoiding cyst recurrence, but this should be addressed with a healthcare expert.
Lifestyle Changes to Prevent Vitamin Deficiency and Cysts
- Healthy Eating Habits: Developing appropriate eating habits is critical for avoiding vitamin shortages. This involves consuming a wide range of nutrient-dense meals while avoiding processed foods rich in sugar and harmful fats.
- Regular Exercise: Regular exercise promotes general health, including joint and tissue health. It also improves circulation, which can help transport nutrients to tissues.
- Avoiding Overuse of Joints: Being attentive to repetitive motions and giving appropriate rest will help to avoid overuse injuries that can lead to cyst development.
When to See a Doctor
- Identifying Serious Symptoms: If you find a lump that is growing, uncomfortable, or hurting with joint movement, consult a doctor for an examination.
- Diagnostic Procedures: A doctor may utilize imaging tests such as X-rays, ultrasounds, or MRI scans to identify a ganglion cyst and rule out alternative possibilities.
- Treatment Planning: According to the diagnosis, a doctor can propose a suitable treatment strategy, which may involve observation, non-surgical therapies, or surgery.
Managing Pain and Discomfort
- Home Remedies: Warm compresses and avoiding activities that increase the pain are two home treatments for dealing with ganglion cyst pain and discomfort.
- Over-the-counter Medications: Over-the-counter pain medications like acetaminophen and ibuprofen can help ease pain and inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy helps improve joint function and decrease the pain associated with ganglion cysts.
Alternative and complementary therapies
- Herbal Remedies: Some herbal medicines, such as turmeric or ginger, include anti-inflammatory characteristics that may help alleviate cyst-related pain.
- Acupuncture: Physiotherapy can help control pain and improve joint function, providing a supplementary therapy to standard methods.
- Massage Therapy: Massage treatment can help reduce tension and increase circulation, perhaps reducing cysts.
Living with Ganglion Cysts
- Coping Strategies: Developing coping mechanisms, such as changing activities and wearing protective gear, can assist in managing life with ganglion cysts.
- Support Systems: A support system, whether it’s friends, family, or a support group, may offer emotional assistance as well as practical information on how to manage the disease.
- Long-Term Management: Long-term care of ganglion cysts involves regular check-ups, following treatment programs, and adopting lifestyle changes to avoid recurrence.
Read More: Is vitamin water good for you? A Comprehensive Guide
Conclusion
Ganglion cysts, while mostly harmless, can cause discomfort and interfere with daily tasks. A well-balanced, vitamin-rich diet, along with a healthy lifestyle, can help to preserve joint and tissue health. If you believe you have a ganglion cyst or are suffering signs of vitamin insufficiency, you should seek medical attention for a correct diagnosis and treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which vitamins are best for joint health?
Vitamin D, Vitamin C, Vitamin E, and Vitamin B12 are the most beneficial vitamins for joint health because they promote bone development, collagen formation, and tissue regeneration.
Do any workouts help with ganglion cysts?
While particular exercises may not be effective in removing the cyst, physical therapy activities can assist in improving joint function and reducing pain.
Can an improper diet lead to ganglion cysts?
While an insufficient diet may not directly induce ganglion cysts, it can lead to vitamin deficiencies, which may damage tissue health and contribute to cyst development.