
Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms: It is also known as the “sunshine vitamin.” Vitamin D is crucial for preserving general health. Millions of individuals worldwide suffer from vitamin D insufficiency, which is surprisingly frequent given its significance. This article explores the signs, causes, and effects of vitamin D deficiency while providing advice on how to maintain sufficient levels of this important mineral.
What is vitamin D, and what are the types of vitamin D?
An essential part of calcium absorption, bone health, and immune system function is played by the fat-soluble vitamin D.
There are two main types of Vitamin D
- Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol)
- Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol)
However, there are advantages for both types, vitamin D3 is more successful in increasing vitamin D levels in the blood.
When we are in the sun, our bodies naturally create vitamin D. But there are other ways to get it, such with specific foods and supplements. Eggs yolks, dairy products with added fortification, and fatty fish are great dietary sources of vitamin D.
Causes of Vitamin D Deficiency
Some of the Important causes of Vitamin D deficiency are as follows:-
Absence of Sunlight Exposure
As all individuals, sunlight serves as their main source of vitamin D. People who live in areas with little sunlight or who spend a lot of time inside are more likely to suffer from deficiencies.
Lack of Nutrition
Weakness may result from a diet deficient in food high in vitamin D. This is especially common in vegans and vegetarians who might not eat seafood or dairy goods that have been fortified.
Health Issues
The body’s capacity to absorb vitamin D may be hampered by a number of illnesses, including chronic renal disease, Crohn’s disease, and celiac disease.
Aspects of Lifestyle
Sunscreen use, having darker skin, and being overweight are some other factors that can hinder the body’s ability to make vitamin D from sunshine.
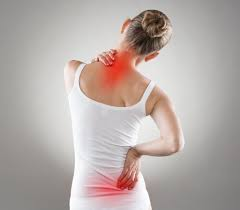
Common Symptoms of Vitamin D Deficiency
Weary and fatigued
Even having enough sleep, and feeling abnormally exhausted or worn out could indicate a vitamin D deficit. This symptom can have a major influence on day-to-day living, although it is typically ignored.
Weakness in the Muscles and Bones
Bone health depends critically on vitamin D. Deficiency can cause weakness in muscles and bone pain, making daily tasks more difficult.
Depression and Shifts in Mood
Anxiety and mood fluctuations have been connected to low vitamin D levels. Getting enough vitamin D can have a positive impact on mental health.
Some of the Physical Symptoms
Recurring infections
Vitamin D impacts immune system performance You may be more prone to infections, such as the flu and colds, if you have a deficit.
Slow Healing of Wounds
Low vitamin D levels may cause your scrapes and bruises to heal more slowly than usual. For healthy tissue repair and wound healing, this vitamin is necessary.
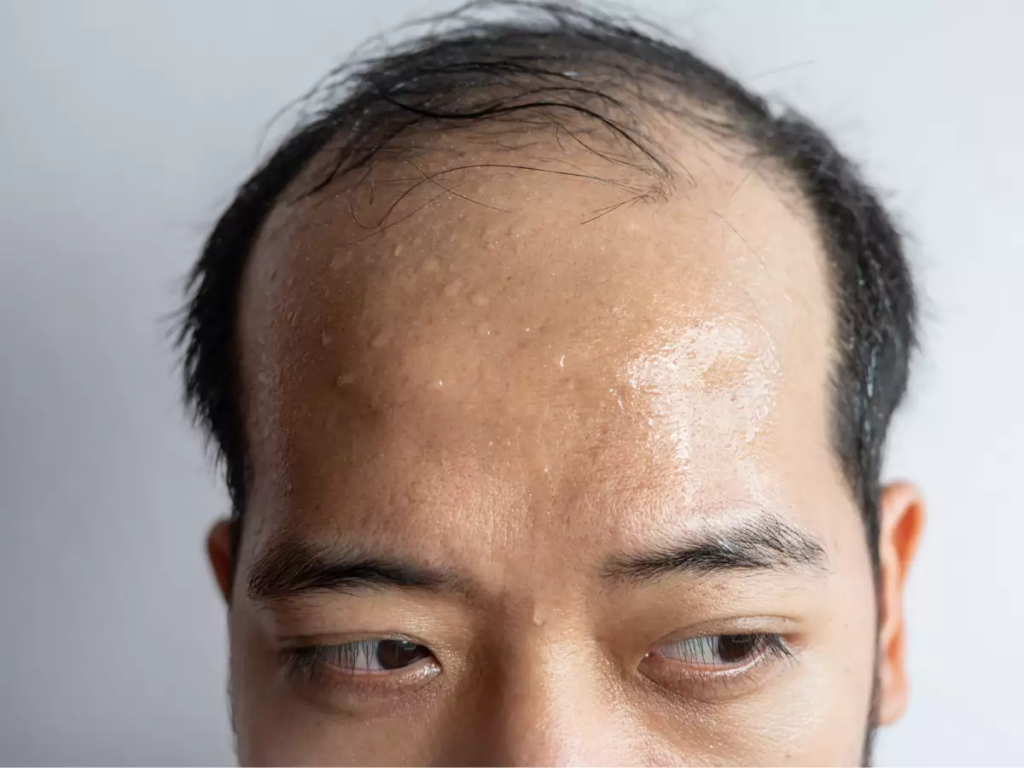
Hair Loss
A vitamin D shortage has been linked to severe hair loss. Even though various causes can cause hair loss, maintaining adequate vitamin D levels helps to support healthy hair.
Impact on Bone Health
The osteoporosis
Bones that are fragile due to osteoporosis might result from a vitamin D shortage. This raises the possibility of bone-related problems such as fractures.
Children’s Rickets
A severe vitamin D deficit in children can result in rickets, a disease that weakens and softens bones and frequently causes skeletal abnormalities.
Enhanced Fracture Risk
Adults who have low blood levels of vitamin D are more likely to break, especially in the hips and back. Maintaining sufficient levels of vitamin D is essential for healthy, strong bones.
Immune System Implications
- Immune System Disorders: Studies indicate that there could be a connection between low levels of sunlight and a higher likelihood of developing autoimmune disorders, including multiple sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis.
- Enhanced Propensity to Contract Infections: Sufficient amounts of vitamin D are necessary for a robust immune system. You may be more susceptible to infections and diseases if you are deficient.
What are the effects on mental health?
- Deficit in Computation: A vital component of brain health is vitamin D. Deficiency has been linked to cognitive decline and a higher chance of developing diseases such as Alzheimer’s.
- Disorders of Anxiety: Problems with anxiety can also be aggravated by low vitamin D levels. Making sure you’re getting sufficient amounts of vitamin D can help reduce anxiety symptoms and enhance your mental health in general.
At-Risk Populations
- Elderly People: Older people are more at risk for vitamin D insufficiency since their skin’s capacity to generate the vitamin declines with age.
- Expectant and Nursing Mothers: Higher amounts of vitamin D are necessary for nursing and pregnant women to promote both their health and the development of their unborn child.
- Individuals with a deeper tone: People with darker skin are more likely to experience vitamin D deficiencies because melanin, the pigment found in darker skin, inhibits the skin’s capacity to synthesize the vitamin from sunshine.
- People Who Are Obese: Vitamin D can be stored in body fat, which reduces the body’s ability to absorb it. Because of this, people who are obese are more prone to be deficient.
Diagnosing Vitamin D Deficiency
- Blood Examinations: Your levels of vitamin D can be determined with an easy blood test. The most popular test, the 25-hydroxyvitamin D test, gives you a quick overview of your vitamin D level.
- Medical Background Information and Physical Assessment: An accurate diagnosis of vitamin D deficiency may also need a physical examination and review of your medical history by the doctor.
Treatment and Management
- Supplements of Vitamin D: One popular and efficient method of treating vitamin D deficiency is with supplements. They are available as liquids, tablets, and capsules, among other forms.
- Nutritional Adjustments: Increasing the amount of meals high in vitamin D that you eat may raise your levels. Egg yolks, dairy products with added nutrients, and fatty fish are all great options.
- Changes in Lifestyle: Increasing your outside time, particularly in the midday when the sun is at its brightest, will help your body naturally produce extra vitamin D.
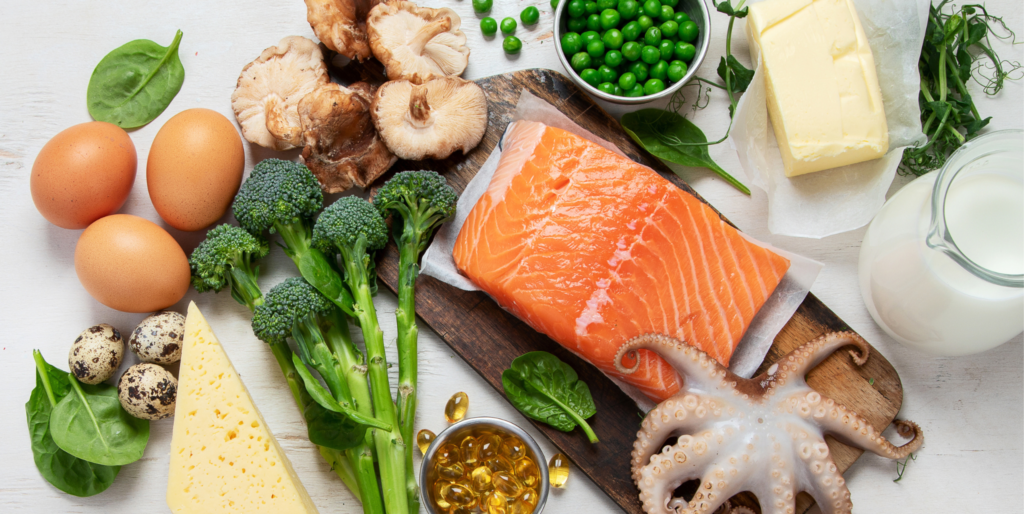

Preventing Vitamin D Deficiency
- Guidelines for Sun Exposure: On multiple occasions per week, try to get 10 to 30 minutes of noon sun exposure. This can assist your body in generating enough vitamin D without raising your chance of developing skin cancer.
- Well-Balanced Diet: To keep your levels in check, a nutritious diet rich in foods high in vitamin D is necessary. If you’re vegetarian or vegan, think about eating fortified foods.
- Frequent Medical Exams: Frequent check-ups can aid in the early detection of vitamin D insufficiency, enabling timely management and treatment.
What are the Myths and Misconceptions
- Vitamin D from Direct Sun Exposure: Even while sunshine is a major source of vitamin D, it might not be enough to rely only on it, particularly in areas with little sunlight.
- Risks of Over-Supplementation: Overconsumption of vitamin D can be detrimental. To prevent toxicity, you must heed your doctor’s recommendations regarding the right dosage.
Read More: Ganglion Cyst Vitamin Deficiency: A Comprehensive Guide
Conclusion
A lack of sunlight can result in a variety of symptoms and health problems. Vitamin D is essential for sustaining general health. To guarantee optimal levels, prevention, and awareness are essential. You can prevent vitamin D insufficiency and preserve maximum health by being aware of its causes, symptoms, and available treatments.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does a vitamin D shortage take to heal?
Depending on the treatment plan and the degree of the insufficiency, recovery times can change. Usually, restoring optimal levels with supplements can take several months.
Can Vitamin D deficiency cause weight gain?
Insufficient amounts of vitamin D can impact hormone control, insulin resistance, inflammation, and metabolism, all of which may contribute to body weight gain. Decreased exercise and higher fat storage may result from these circumstances. Deficiency is unable to trigger weight gain directly, but it could impact the circumstances that encourage it.
1 thought on “Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms: A Comprehensive Guide”